Understanding Different Types of Computer Storage
Discover the various types of computer storage, including HDDs, SSDs, and cloud storage, and understand their unique features and benefits.
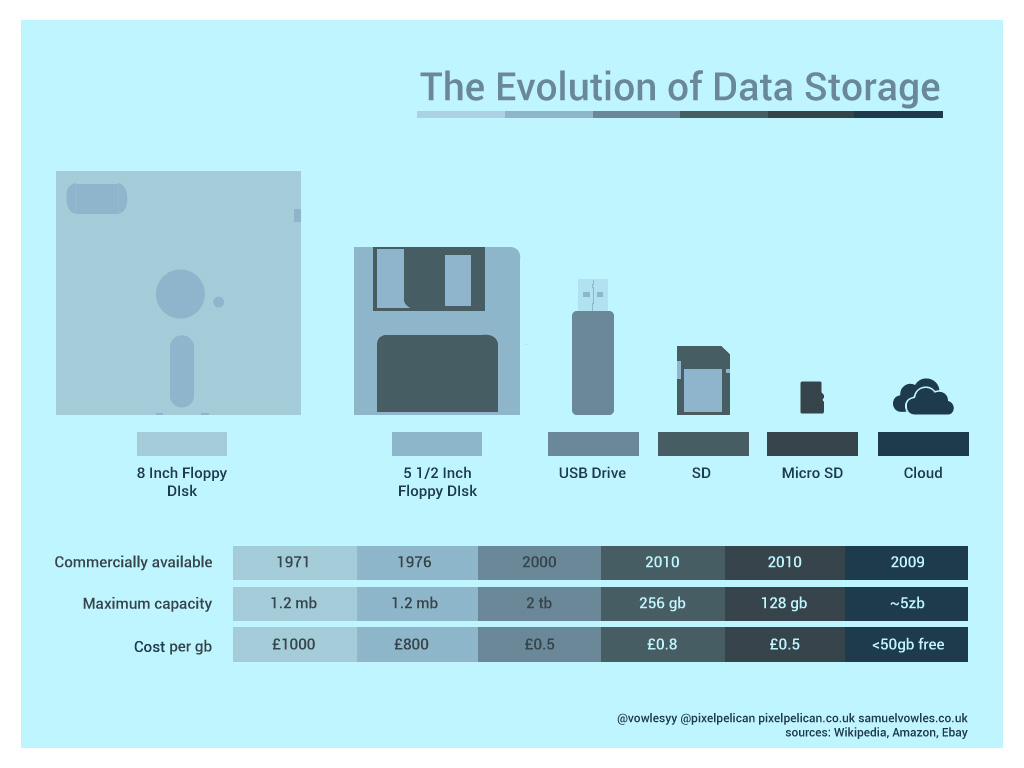
Introduction to Computer Storage
Understanding different types of computer storage is crucial for both casual users and professionals. Storage devices are essential for saving and retrieving data, and they come in various forms, each with unique characteristics. Whether you're storing documents, photos, or software, knowing the differences can help you make informed decisions. Computer storage can be broadly categorized into primary and secondary storage, each serving distinct purposes. This article will delve into these categories, highlighting the advantages and limitations of each type. By the end, you'll have a clearer understanding of which storage solutions are best suited for your needs.
Primary Storage: RAM
Random Access Memory (RAM) is a type of primary storage that computers use to store data temporarily. Unlike other storage types, RAM is volatile, meaning it loses all stored information when the computer is turned off. RAM is crucial for the system's performance, as it provides quick read and write access to the CPU. The more RAM a computer has, the more efficiently it can handle multiple tasks simultaneously. However, RAM is not suitable for long-term data storage. It's best used for running applications and processes that require immediate access to data. Understanding RAM's role can help you optimize your computer's performance.
Secondary Storage: Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs) are a common type of secondary storage used in many computers. They store data magnetically on spinning disks, allowing for substantial storage capacity at a relatively low cost. HDDs are non-volatile, meaning they retain data even when the computer is turned off. They are ideal for storing large files, such as videos, photos, and software. However, HDDs are slower compared to other storage types like SSDs. They are also more prone to physical damage due to their mechanical parts. Despite these drawbacks, HDDs remain a popular choice for budget-conscious users who need ample storage space.
Secondary Storage: Solid State Drives (SSDs)
Solid State Drives (SSDs) are another type of secondary storage, known for their speed and durability. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts, which makes them faster and more reliable. They use flash memory to store data, allowing for quicker boot times and faster file access. SSDs are ideal for users who prioritize performance and are willing to invest in higher-quality storage. However, SSDs are generally more expensive per gigabyte compared to HDDs. They also have a limited number of write cycles, although this is less of an issue with modern SSDs. For those who need speed and reliability, SSDs are an excellent choice.
Hybrid Drives: Combining HDD and SSD
Hybrid Drives or Solid State Hybrid Drives (SSHDs) combine the best features of both HDDs and SSDs. They include a small amount of SSD storage for frequently accessed data and a larger HDD for general storage. This combination offers a balance between performance and capacity. Hybrid drives are designed to improve boot times and application load times without the high cost of a full SSD. They are a good option for users who need a large amount of storage but also want faster access to critical files. While not as fast as pure SSDs, hybrid drives provide a cost-effective solution for many users.
External Storage: USB Drives and External Hard Drives
External storage devices like USB drives and external hard drives offer portable and flexible storage solutions. USB drives are small, easy to carry, and perfect for transferring files between computers. They come in various capacities, making them suitable for both small and large files. External hard drives, on the other hand, provide more significant storage capacity and are ideal for backups and additional storage needs. These devices are plug-and-play, requiring no installation, and can be used with multiple devices. They offer a convenient way to expand storage without modifying the internal components of your computer.
Cloud Storage: The Future of Data Storage
Cloud storage has become increasingly popular due to its convenience and accessibility. It allows users to store data on remote servers, accessible from any device with an internet connection. Cloud storage services offer various plans, from free options with limited storage to premium plans with extensive capacity. The main advantage of cloud storage is its ability to provide seamless data access and backup solutions. However, it requires a reliable internet connection and raises concerns about data privacy and security. For users who need access to their files from multiple locations, cloud storage is an invaluable resource.
Network Attached Storage (NAS)
Network Attached Storage (NAS) is a specialized storage solution designed for home and small business networks. NAS devices are essentially dedicated file servers that connect to a network, allowing multiple users to access shared data simultaneously. They offer a centralized storage location, making data management and backup more straightforward. NAS devices can be configured with multiple drives for redundancy and increased capacity. They are ideal for environments where data sharing and collaboration are essential. While NAS requires an initial investment and some technical knowledge to set up, it provides a robust and scalable storage solution.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Storage Solution
Choosing the right storage solution depends on various factors, including your budget, performance needs, and storage capacity requirements. Primary storage like RAM is essential for system performance but is not suitable for long-term data storage. Secondary storage options like HDDs and SSDs offer different balances of cost, capacity, and speed. Hybrid drives provide a middle ground, while external storage offers portability and flexibility. Cloud storage provides convenience but requires an internet connection, and NAS offers centralized, network-based storage. By understanding these different types of storage, you can make an informed decision that best suits your needs.